ADA Compliance for Law Firm Websites in 2022

Legal reasoning involves applying the law to the facts to determine the rights and duties of those involved in a situation. Lawyers frequently take the position that the application of rules should settle disputes and that policies will be considered, if at all, only when there is a high degree of uncertainty surrounding the applicability of the rule. The lawyer might take the position that it is always preferable to seek the result that would further the underlying policies, even if that result would be contrary to the clear language of the rules.
But what if no explicit rules currently exist?
That is the issue with website compliance under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). The Act does not offer specific guidelines to follow; however, websites are expected to be easily accessible to everyone, including those who are disabled. The failure to create an ADA-compliant website could expose an organization to discrimination lawsuits, financial liabilities, and severe damage to its reputation.
What is the ADA?
The ADA compels certain businesses, including banks, hotels, restaurants, public transit, law firms, and others to make accommodations for people with disabilities. According to the National Law Review, the Act is divided into three parts:
- Title I prohibits employers from discriminating against employees based on disability and requires them to provide reasonable accommodation to certain employees under specific circumstances.
- Title II covers state and local governments.
- Title III covers “places of public accommodation,” which the ADA does not define, but are generally private businesses or organizations that provide goods, services, facilities, privileges, or accommodations to the public. These places commonly include schools, restaurants, health care providers, social service agencies, law firms, and more.
The ADA is commonly associated with physical locations and the accommodations that certain businesses must make for people with disabilities, which include wheelchair accessibility, reserved parking, and service animals. Companies that fall under ADA Title I and operate 20 or more weeks per year with at least 15 full-time employees, or Title III – those that fall under the category of public accommodation – must be ADA-compliant.
Although physical “brick-and-mortar” locations are nearly always considered places of public accommodation, the debate is ongoing as to whether a business’s website is a place of accommodation. If so, the digital content must be accessible to all users.
A law firm website must be designed so that those who are disabled can access it easily to comply with ADA requirements. While there are no well-defined regulations that describe precisely what an ADA-compliant website should include, businesses that fall under ADA Title I or ADA Title III are required to develop a website that offers “reasonable accessibility” to people with disabilities.
Compliance tools & plugins
Because the ADA doesn’t offer specific guidelines for website compliance, many organizations follow the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.0 (WCAG), updated to 2.1 in 2018. While WCAG isn’t a legal requirement, its requirements have been followed in the European Union and other nations since 1999 and still serves as a reference for businesses that want to improve accessibility to their website.
Under WCAG 2.1, website accessibility concerns generally fall into four groups. These include issues that are:
- Perceivable – issues that affect users’ ability to locate and process the information on a website, e.g., many visually-impaired individuals use screen readers to distinguish between the text and the background to help them navigate online content.
- Operable – challenges that impair users’ ability to navigate a site, e.g., functions and navigations such as online forms should be accessible via keyboard-only commands, and users who need additional time to complete them should be allowed to do so.
- Understandable – users should be able to comprehend the information on the site, e.g., error messages that provide an explanation and directions for correcting an error should be offered.
- Robust – can be interpreted by various devices and platforms according to the varying needs and abilities of users, e.g., the alt text that should pop up to let users know what it is when read by assistive technology when they hover over an image.
Here are more suggestions regarding what to include to help ensure ADA website compliance:
- “Alt” tags for every media file and map
- Descriptive HTML tags for online forms
- Hyperlinks with descriptive anchor text
- “Skip navigation” links on all website pages
- Heading tags to organize text
- Accessible PDF files
- Subtitles, transcripts, and audio descriptions for videos
- Accessible fonts for all applications
- HTML tables with column headers, row IDs, and cell information
- Captions written in English for audio files
- Call-to-action buttons with easily accessible names and ARIA labels
- A website accessibility policy
- Easy to find contact information
Meeting these guidelines will make a firm’s website more accessible to those with vision or hearing impairments, as well as cognitive, language, or learning disabilities.
Court rulings regarding website ADA compliance
According to the American Bar Association (ABA), the number of accessibility-related lawsuits filed against websites has increased dramatically in recent years. Plaintiffs are basing these lawsuits on two legal theories:
- Title IIIs “equal access and general nondiscrimination mandate
- A requirement that places of public accommodation must provide auxiliary aids and services as necessary (for no extra charge)
Although neither Title III nor its regulations mention websites and mobile applications, the phase “auxiliary aids and services” includes “accessible electronic and information technology,” which covers websites and mobile apps.
Image by Seyfarth via adatitleiii.com
A recent ABA analysis of court filings related to ADA website compliance found:
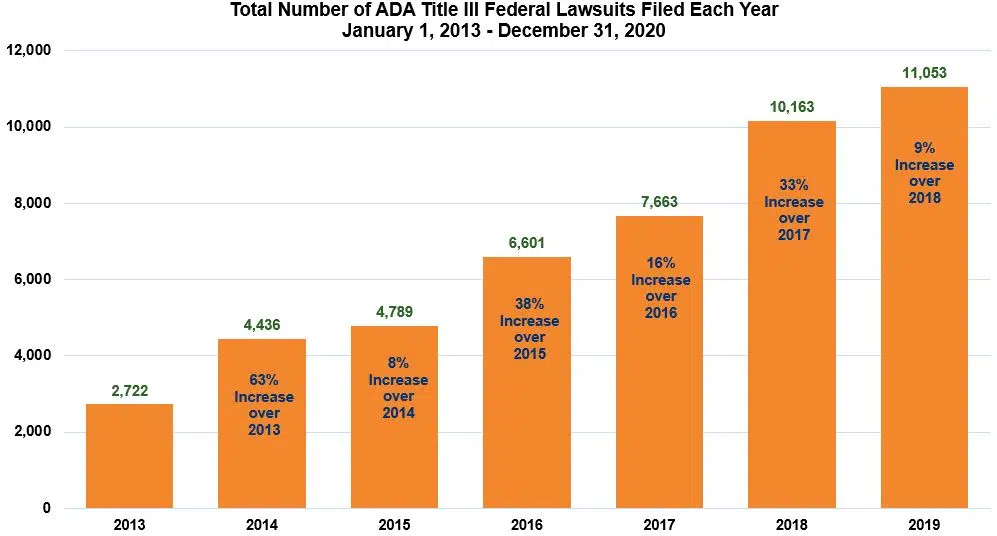
- Federal courts across the country were inundated with more than 8,000 website accessibility lawsuits between 2017 and 2020.
- In 2020, three states – New York, Florida, and California – brought more than 85 percent of all the ADA website compliance lawsuits.
- Since 2018, website and mobile app accessibility disputes have accounted for approximately 20 percent of all ADA Title III cases initiated in federal courts, which now regularly exceed 10,000 suits each year.
These statistics do not consider a significant number of website and mobile app cases pursued in state courts, cases settled before filing in court, and DOJ enforcement proceedings that are resolved prior to court filing.
Here are some examples of court rulings related to ADA compliance and websites:
Gil v. Winn-Dixie Stores Inc.
In June 2107, a Florida court ruled in favor of a blind plaintiff who brought an ADA violation lawsuit against Winn-Dixie. The man claimed that aspects of the supermarket chain’s site weren’t compatible with screen readers, leaving him unable to order his medications online or download rewards cards. The trial court agreed that the website was inaccessible to those with impaired vision and ordered that it be brought into compliance with the WCAG 2.0 Level AA.
Although Winn-Dixie complied with the court order, in April 2021, the Eleventh Circuit Court of Appeals overturned the trial court’s decision, finding that Winn-Dixie was not in violation of the ADA because it did not need accessibility aids to conduct business. After that, however, Winn-Dixie posted an accessibility statement on its website that commits to adhere to WCAG 2.0 AA by using testers from the disability community to check the accessibility of their website periodically.
Robles v. Domino’s Pizza
Domino’s Pizza lost a website accessibility lawsuit in 2019 after years of exhaustive litigation when a federal district court in California granted the plaintiff’s motion for summary judgment after it determined that the website was indeed not fully accessible. The court ordered Domino’s to make its website compliant with the WCAG 2.0 to connect customers to the goods and services of Domino’s physical restaurants.
The court held that the ADA applied to Domino’s website and app because the Act requires places of public accommodation, like Domino’s, to offer auxiliary aids and services to make visual materials available to blind individuals. Although customers primarily access the Domino’s website and app outside its physical restaurants, the court found that the Act pertains to the services of public accommodation, not services in a place of public accommodation.
Andrews v. Blick Art Materials
In 2017, Victor Andrews, who is blind, filed a lawsuit against Blick Art Materials for website inaccessibility. Andrews alleged that because Blick’s website was inaccessible, he could not navigate and purchase items on the defendant’s website independently. When Blick made a motion to dismiss the lawsuit, Judge Jack Weisenstein denied it and made this statement:
Today, internet technology enables individuals to participate actively in their community and engage in commerce from the comfort and convenience of their home. It would be a cruel irony to adopt the interpretation of the ADA espoused by Blick, which would render the legislation intended to emancipate the disabled from the bonds of isolation and segregation obsolete when its objective is increasingly within reach.
The ruling in this case and others illustrates that businesses need to consider their websites equivalent to a place of public accommodation, which puts them at risk of being sued, even without explicit web accessibility regulations.
Latest DOJ guidelines
In 2010, the Department of Justice (DOJ) launched a rulemaking process to address ADA requirements for website accessibility, including technical standards for accessible websites. However, that effort stalled for seven years during the Obama administration (even though the administration continued to pursue investigations and enforcement actions against businesses with inaccessible websites).
The Trump administration abandoned the process to interpret the ADA entirely in 2017. In 2018, the DOJ revealed that it would not give official guidance regarding website accessibility under the Act, releasing this statement:
The Department is evaluating whether promulgating regulations about the accessibility of Web information and services is necessary and appropriate. Such an evaluation will be informed by additional review of data and further analysis. The Department will continue to assess whether specific technical standards are necessary and appropriate to assist covered entities with complying with the ADA.
Since the DOJ’s withdrawal, the number of lawsuits involving website accessibility increased dramatically, raising awareness regarding website accessibility among businesses but also causing confusion surrounding what features an ADA-compliant website should include. As a result, numerous website accessibility consulting companies emerged promising inexpensive solutions. However, some have been challenged in court.
In June 2018, some bipartisan members of the U.S. House of Representatives sent a letter to Attorney General Jeff Sessions encouraging the DOJ to release clear website accessibility regulations to diminish the unclear nature of current legislation. On September 25, 2018, the DOJ responded by stating that, at this time, the DOJ would not be issuing web accessibility regulations under the ADA: “The Department has consistently taken the position that the absence of a specific regulation does not serve as a basis for noncompliance with a statute’s requirements.”
In March 2022, the DOJ issued further web accessibility guidance under the ADA. The “new” guidance references both the WCAG – which are voluntary – and Section 508 standards, which set standards for federal websites, and indicates that the DOJ supports the notion that sites of public accommodation must be accessible, and in the absence of explicit regulations, websites can be flexible in how they choose to comply with the ADA’s requirements. However, the guidance does not clarify what such flexibility or choice entails and– not necessarily the direction regulation-seekers are looking for, since it provides no substantially new information regarding the vagueness of website accessibility requirements under the ADA.
Final thoughts
As accessibility regulations for websites remain unclear, it can be easy for organizations to assume that they cannot be sued for noncompliance. However, with no specific standards to follow, law firms and other businesses must do their best to interpret the ADA, practice website accessibility as they see fit, and try to avoid website accessibility-related lawsuits.
One more thing to consider: ambiguity runs both ways, and even though an organization might think its website is accessible, a disabled person might think otherwise, providing the grounds for a lawsuit. Organizations aren’t granted immunity simply because of a lack of clarity in legislation. Instead, uncertainty allows for interpretation by anyone, including the courts.